
There are three types of network transmission media: coaxial cables, network cables, and optical fibers. As an important carrier for network signal transmission, network cables are composed of two copper wires with an insulating protective layer. Two insulated copper wires are twisted together at a certain density. The radio waves radiated by each wire during transmission will be offset by the radio waves emitted by the other wire, effectively reducing the degree of signal interference. Therefore, it is also called double Twisted pair (TP).
Classified by different performance
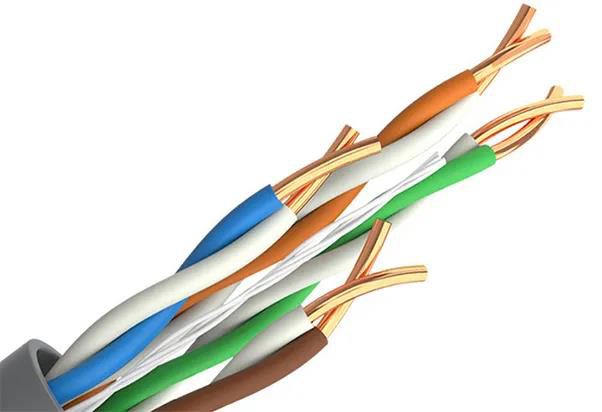
▶Category 5e network cable CAT5E
Category 5e network cable is the most commonly used type of network cable in life. Because the wiring is simple, the price is much cheaper than other network cables. The transmission rate is up to 100Mbps, and it is durable and does not drop out.
The international network cable is made of oxygen-free copper with a copper core and a copper core diameter of 0.51mm, which stably supports 100M network. Because the resistance of oxygen-free copper is the smallest compared with others, the resistance per hundred meters is about 9.5Ω. The resistance is small, the transmission rate is relatively high, and the service life is relatively long. Generally, we choose household network cables. For the sake of economy, we can choose this type of network cable.
▶Category six network cable CAT6
Category 6 network cable is an upgraded version of Category 5e network cable. It has high transmission efficiency and various parameters have been greatly improved compared with Category 5e.
The transmission rate reaches 1000Mbps. Compared with Category 5e cables, an insulating cross frame is added in the middle, the isolation effect is better, and the diameter of the cable is also thicker.
Copper core wire diameter 0.58mm, high-quality thickened conductor core, thickened pure copper shrapnel, gold-plated contacts, crystal clear and good toughness, PE middle quilt and PVC outer quilt material, not only wear-resistant and anti-bending, but also improved The service life of the wire core. Those who have higher requirements for network transmission may wish to try this type of network cable, and the network speed output of this type of network cable is also relatively stable.
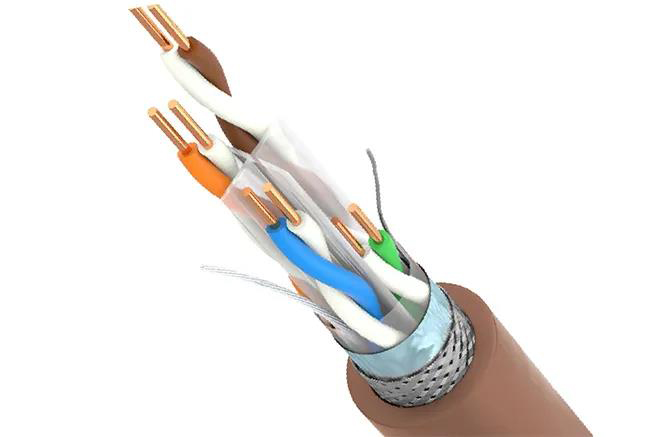
▶Category 6e network cable CAT6E
Category 6e cable is an upgraded version of Category 6 cable, so it is also called "enhanced Category 6 cable". It has better performance than Category 6 cable in aspects such as external crosstalk. Compared with Category 6 network cables, Category 6e network cables have a larger outer diameter, heavier weight, and a larger minimum bending radius. Category 6e cables can still operate normally in high-performance cabling systems of -20 to 60°C. When the transmission rate is 10Gbps, the transmission distance can reach 100m. At the same time, it is backward compatible with all previous categories.
▶Category 7 network cable CAT7
Category seven network cables use oxygen-free copper as the core. The transmission frequency can reach at least 600MHz, the transmission rate can reach 10Gbps, and the performance is excellent.
Pure copper wire core, eight cores and seven strands, can stably transmit 10G network signals.
Zero signal attenuation, high speed, high transmission, strong performance, stable and barrier-free network transmission, faster, more stable, safer and more environmentally friendly.
The performance has been greatly improved compared to Category 5e and Category 6, but the wiring construction is slightly complicated.
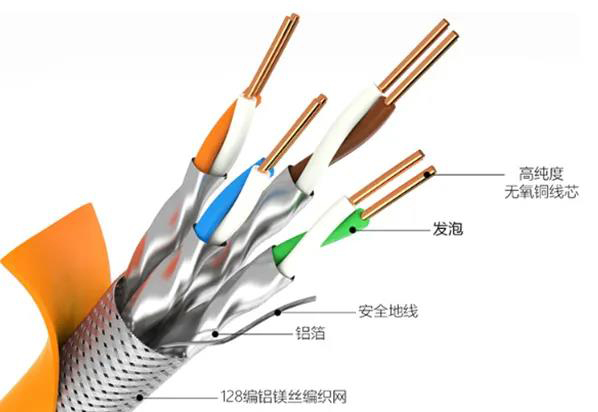
Classified by signal shielding ability
Shielding network cables is mainly aimed at environments with strong interference. Interference environments will cause network cable transmission signals to be intermittent or even interrupted, making it impossible to transmit signals normally. The use of shielded network cables can resist interference very well, maintain normal transmission, and have good confidentiality performance. The shielding structure of shielded wiring has inherent advantages in reducing mutual interference between cables. It can not only shield external electromagnetic signals, but also aluminum foil. It blocks the electromagnetic leakage of the cable itself, does not emit interference signals and affects the work of other cables, and prevents information from being eavesdropped.
▶UTP
Unshielded Twisted Pair is an unshielded twisted pair. It is used for ordinary network applications with a transmission bandwidth below 250MHz and no special performance requirements. It has no shielding jacket, small diameter, light weight, easy to bend, easy to construct and maintain, and cheap. . However, the highest performance limit of this type only supports Category 6 cabling systems.
▶STP
Shielded twisted pair is an independently shielded twisted pair. An aluminum foil layer is added outside the core wire. Each pair of wires has an aluminum foil shielding layer to reduce signal attenuation. Each 4-pair wire package also has a metal braided shielding layer, which has reached the structural standards of Category 7 network cables. It is suitable for high-speed network and high-security transmission, can support future application updates, can unify the wiring platform, and can transmit multiple media information together.
▶FTP
Foiled Twisted Pair is an aluminum foil shielded twisted pair. It has the advantages of large bandwidth, certain anti-interference ability, reduced signal attenuation, recycling, low smoke, halogen-free, and environmental protection.
▶SFTP
Shielded Foiled Twisted Pair is a double-shielded twisted pair, which adds a braided mesh to the STP aluminum foil. Usually aluminum-magnesium wire braided mesh or tinned copper mesh is used, and the outer layer is PVC outer cover. Generally speaking, there are two layers of shielding layers, and there must be insulation isolation between the two layers of shielding layers. Its advantage is that it effectively reduces environmental magnetic field, signal interference, and low internal signal attenuation; its disadvantage is that it is poor in flexibility and expensive. This kind of wire with anti-interference and highly confidential transmission is suitable for professional wiring projects in special environments.
▶ASTP
Armored Shielded Twisted Pair (armored twisted pair shielded network cable) is a special double-shielded network cable. Based on the above double-shielded cable, the outer layer is a steel tape armored layer. When used, the steel tape Both ends of the armor layer are grounded, and one end of the innermost shield is grounded. In addition to the effect of double shielded wires, it has high strength and can be used in wiring systems with frequent rodent infestations or explosion-proof requirements. Generally, shielded wires are more expensive in cost and installation than unshielded wires, and their bending performance is slightly worse. But it is suitable for integrated wiring in some special environments and screen-disabled systems. Everyone can make a reasonable choice after understanding their own situation to optimize costs and wiring effects.
Classified by number of wire strands
▶Single strand copper wire
Due to its structural reasons, single-stranded copper wires are correspondingly harder than multi-stranded wires. They are mainly used as engineering wiring. Network cable signals are high-frequency currents that only flow on the surface of the conductor (skin effect). They are generally used For fixed laying (such as pipe lines, etc.). Compared with multi-strand copper wire, single-strand copper wire is more convenient in terms of line connectors and equipment wiring. Multi-strand copper wire generally requires crimping or welding wire noses, etc. However, multi-strand copper wire is more expensive than single-strand copper wire.
▶Multiple stranded copper wire
Multi-stranded copper wire is a thin conductor wire with good toughness and will not cause the conductor to break due to repeated bending. It is mostly used for control lines. It is suitable for occasions where wires need to follow the movement (such as general distribution boxes and cabinet doors) and where multiple wires are laid together (to facilitate wire laying and wire bundle forming). The multi-stranded copper core makes the current flow path irregular and generates fluctuations, which in turn causes electromagnetic interference and affects the quality of the transmitted signal.
Network cable selection
Hand feeling: High-quality network cables generally use copper wire as the conductor core, which is relatively soft. Inferior-quality conductors have other metal elements added to them, which are relatively hard and difficult to bend, and are easy to break during use.
Cut with a knife: Remove the plastic outer sheath to expose the core wire. The white core wire is gray. Fake products are usually pure white or have no obvious color. Good network cables have moderate winding density and the direction is counterclockwise.
Use fire: Use high temperature test to show that the rubber on the outside of genuine network cables will not soften. The rubber on the outside of genuine network cables is flame retardant, while some fake ones are not flame retardant and do not meet safety standards. , the hardness of iron is very high, and it will not soften quickly when heated with fire.
There are three types of network cable standard production line sequences: T568A, T568B and the third type.
The T568A line sequence is: white-green, green, white-orange, blue, white-blue, orange, white-brown, brown.
The T568B line sequence is: white-orange, orange, white-green, blue, white-blue, green, white-brown, brown.
The third line sequence is: white-green, green, white-orange, white-brown, brown, orange, blue, white-blue.
The network cable has 4 pairs of twisted pairs. For 100M bandwidth, four wires 1, 2, 3, and 6 can transmit signals. Among them, 1 and 2 are used as the sending end of the data, and 3 and 6 are used as the receiving end of the data, so do When using network cables, just make sure that group 1 and 2 and group 3 and 6 have the same color sequence and they will be connected. Gigabit Ethernet networks usually use all eight cores. For example, a Category 6 and Category 6e cable requires not only 1 3 2 6 but also all eight cores, otherwise the network operation will be unstable.
Application of network cable
There are two main types of Ethernet connections: straight-through cables and crossover cables.
▶Straight-through cable
Straight-through cables are used to connect computers to switches, HUBs (hubs), etc.
The crystal heads at both ends follow the T56A or T568B standard, and T568B is usually used more often. The straight-through cable connection method of Ethernet 100M network cable and Gigabit network cable is the same.
▶Crossover cable
Used to connect computers to computers, switches to switches, etc.